Monkeypox is an infectious disease caused by the monkeypox virus. The disease was first identified in laboratory monkeys, hence its name, but in its natural state it seems to infect rodents more often than primates. The disease, which is a similar to but milder than Smallpox, is transmitted to people from various wild animals. It however, has limited secondary spread through human-to-human transmission. It produces pox lesions on the skin and is closely related to smallpox but is not nearly as deadly as smallpox was.
History Of Monkeypox
The virus was first identified in the State Serum Institute in Copenhagen, Denmark, in 1958 during an investigation into a pox-like disease among monkeys. Human monkeypox was first identified in humans in 1970 in the Democratic Republic of Congo (then known as Zaire) in a 9 year old boy in a region where smallpox had been eliminated in 1968. Since then, the majority of cases have been reported in rural, rainforest regions of the Congo Basin and western Africa, particularly in the Democratic Republic of Congo, where it is considered to be endemic. In 1996-97, a major outbreak occurred in the Democratic Republic of Congo.
In the spring of 2003, monkeypox cases were confirmed in the Midwest of the United States of America, marking the first reported occurrence of the disease outside of the African continent. Most of the patients had had close contact with pet prairie dogs.
In 2005, a monkeypox outbreak occurred in Unity, Sudan and sporadic cases have been reported from other parts of Africa. In 2009, an outreach campaign among refugees from the Democratic Republic of Congo into the Republic of Congo identified and confirmed two cases of monkeypox. Between August and October 2016, a monkeypox outbreak in the Central African Republic was contained with 26 cases and two deaths.
Source – WHO
Signs and symptoms of Monkeypox
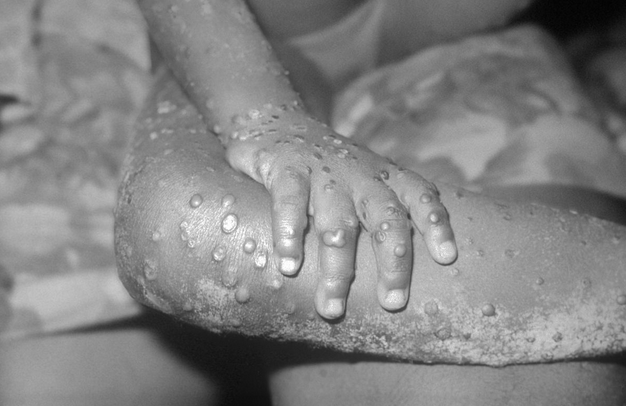
In humans, the symptoms of monkeypox are similar to but milder than the symptoms of smallpox. Monkeypox begins with fever, headache, muscle aches, and exhaustion. The main difference between symptoms of smallpox and monkeypox is that monkeypox causes lymph nodes to swell (lymphadenopathy) while smallpox does not. The incubation period (time from infection to symptoms) for monkeypox is usually 7−14 days but can range from 5−21 days.
The illness begins with:
- Fever
- Headache
- Muscle aches
- Backache
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Chills
- Exhaustion
Within 1 to 3 days (sometimes longer) after the appearance of fever, the patient develops a rash, often beginning on the face then spreading to other parts of the body.
Lesions progress through the following stages before falling off:
- Macules
- Papules
- Vesicles
- Pustules
- Scabs
The illness typically lasts for 2−4 weeks. In Africa, monkeypox has been shown to cause death in as many as 1 in 10 persons who contract the disease.
Source – cdc
Transmission of Monkeypox
Infection of index cases results from direct contact with the blood, bodily fluids, or cutaneous or mucosal lesions of infected animals. In Africa human infections have been documented through the handling of infected monkeys, Gambian giant rats and squirrels, with rodents being the major reservoir of the virus. Eating inadequately cooked meat of infected animals is a possible risk factor.
Secondary, or human-to-human, transmission can result from close contact with infected respiratory tract secretions, skin lesions of an infected person or objects recently contaminated by patient fluids or lesion materials. Transmission occurs primarily via droplet respiratory particles usually requiring prolonged face-to-face contact, which puts household members of active cases at greater risk of infection. Transmission can also occur by inoculation or via the placenta (congenital monkeypox). There is no evidence, to date, that person-to-person transmission alone can sustain monkeypox infections in the human population.
Source – WHO
Prevention of Monkeypox
Avoid contact with animals that could harbor the virus (including animals that are sick or that have been found dead in areas where monkeypox occurs).
Avoid contact with any materials, such as bedding, that has been in contact with a sick animal.
Isolate infected patients from others who could be at risk for infection.
Monkeypox is preventable as long as people avoid direct contact with infected animals and people. Vaccination against smallpox seems to afford about an 85% chance of avoiding the infection. There is no commercially available vaccine specifically for monkeypox.
Diagnosis of Monkeypox
The diagnosis of monkeypox is often made presumptively in Africa by the patient’s history and the exam that shows the pox lesions, however, a definitive diagnosis is made by PCR, ELISA, or Western blotting tests that are usually done by the CDC or some state labs. Definitive diagnosis is important to rule out other possible infectious agents like smallpox.
Treatment of Monekypox
Treatment may consist of immediate vaccination with smallpox vaccine because monkeypox is so closely related to smallpox. Treatment with an antiviral drug or human immune globulin has been done.
In general, the prognosis for monkeypox is good to excellent as most patients recover. The prognosis may decrease in immunocompromised patients, and patients with other problems such as malnutrition or lung disease may have a poorer prognosis.
Source – medicinenet